

WiFi is our commonly used wireless network, and WiFi6 is the sixth generation of wireless network technology. This is a wireless LAN technology created by the Wi-Fi Alliance in the IEEE802.11 standard. At present, the one we use the most is WiFi5.
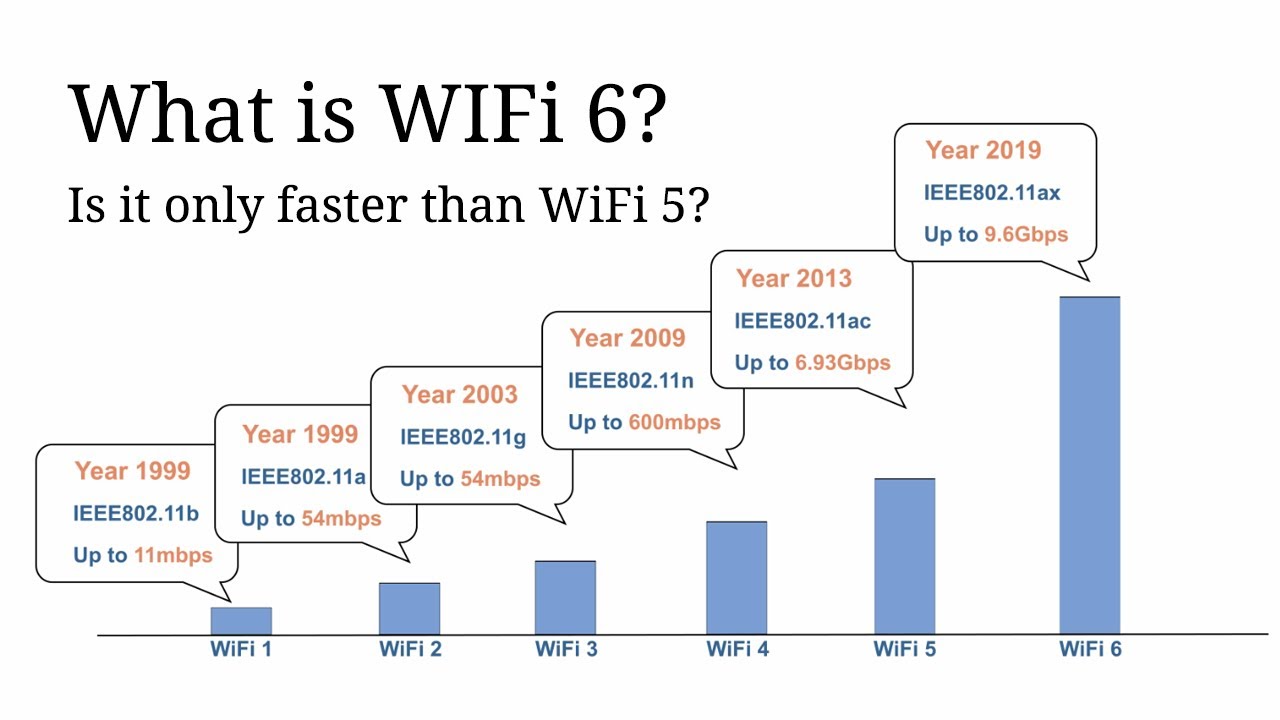
To know the origin of the name WiFi6, we must first talk about the Wi-Fi Alliance. Founded in 1999, the Wi-Fi Alliance was originally called the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA). In October 2002, it officially changed its name to the Wi-Fi Alliance, or WiFi for short. At the end of 2018, the WiFi Alliance announced that it would change the nomenclature of the WiFi standard and would no longer use the technical terminology of 802.11 electrical engineering. It will simply name the latest 802.11ax standard WiFi6.
The main advantages of WiFi6
1.WiFi6 is faster
The main advantage of WiFi6 is reflected in its speed. After 20 years of development, WiFi6 is already 827 times faster than the first generation of wireless network technology WiFi1. Compared with the previous generation 802.11ac WiFi5, the maximum transmission rate of WiFi6 has been increased from the previous 3.5Gbps to 9.6Gbps, and the theoretical speed has increased by nearly 3 times.
In the frequency band, WiFi5 only involves 5GHz, while WiFi6 covers 2.4/5GHz, covering low-speed and high-speed devices. WiFi6 supports 1024-QAM, higher than WiFi5's 256-QAM, with higher data capacity and corresponding data transmission speed.
2.WiFi6 has lower latency
Previous generations of WiFi have been using OFDM technology (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) with sequential order. After injecting the new OFDMA technology into WiFi6, the wireless router can connect to multiple devices, effectively solving the problems of data congestion and delay.
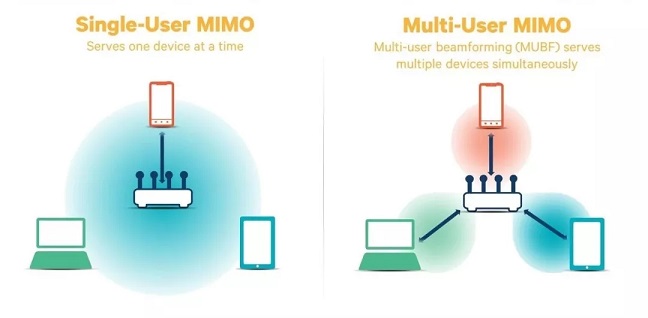
In addition, the maximum spatial data stream that WiFi6 can support has increased from 4 to 8 in WiFi5, that is to say, it can support up to 8×8 MU-MIMO, which is also one of the important reasons. More importantly, WiFi6 uses OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) technology, which is an evolved version of the OFDM technology used by WiFi5. It combines OFDM and FDMA techniques and uses OFDM to parent the channel. Afterwards, some subcarriers are loaded with transmission techniques for transmitting data.
3.WiFi6 has a larger capacity
WiFi6 also introduces the BSSColoring coloring mechanism to add labels to each device connected to the network and add corresponding labels to its data. When transferring data, there is a corresponding address, which is transferred directly to that location without confusion.
Multi-user MU-MIMO technology allows a computer network to share channels with multiple terminals at a time, so that multiple mobile phones/computers can access the Internet at the same time, from the previous inefficient queuing sequence delivery method to the efficient "hand in hand". Combined with OFDMA technology, each channel under the WiFi6 network can perform efficient data transmission, improve the network experience in the case of multiple users, and can better meet the needs of WiFi hotspots. It is not easy to freeze when used by multiple users, and has a larger capacity.
4. WiFi6 is more secure
WiFi6 devices can only pass WiFiAlliance certification if they adopt the new generation encryption security protocol WPA3 protocol. In this way, brute force attacks, brute force attacks, etc. can be prevented, and the security is further guaranteed.
5.WiFi6 saves more power
WiFi6 introduces TARget wake-up time (TWT, target wake-up time) technology, which enables devices and wireless routers to actively plan communication time, thereby reducing the use of wireless network antennas and signal search time, which means it can reduce power consumption to a certain degree. To some extent, the battery life is improved, and it is estimated that the power consumption can be reduced by 30%. But the technology is mostly used in smart homes right now.
Is it time to replace your WiFi6 router?
At present, there are relatively few types of WiFi6 routers, and their prices are much more expensive than ordinary routers. Second, users' wireless Internet access devices must support WiFi6 routers, and there aren't many such devices on the market. Secondly, WiFi6 has higher requirements on network bandwidth. In order to give full play to the role of WiFi6, at least gigabit bandwidth is required, and most network environments have not yet met this requirement. Overall, WiFi6 is still in its infancy, and there is still a long way to go. But in the near future, with the innovation and upgrading of technology and equipment, WiFi6 will be widely used in our lives.








